We need to apply Faraday's Law
in order to find the differential equation for the circuit. We choose a reference current to be in the clockwise direction. Then 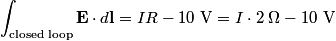 and 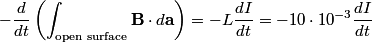 Therefore, 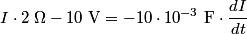 The solution to this differential equation with the initial condition that 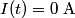 is is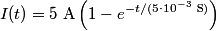 The voltage across the inductor is not well-defined; because the electric field is nonconservative, the integral of 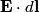 depends on the path that you take. However, the problem clarifies this with the phrase ``as seen on an oscilloscope." depends on the path that you take. However, the problem clarifies this with the phrase ``as seen on an oscilloscope." |